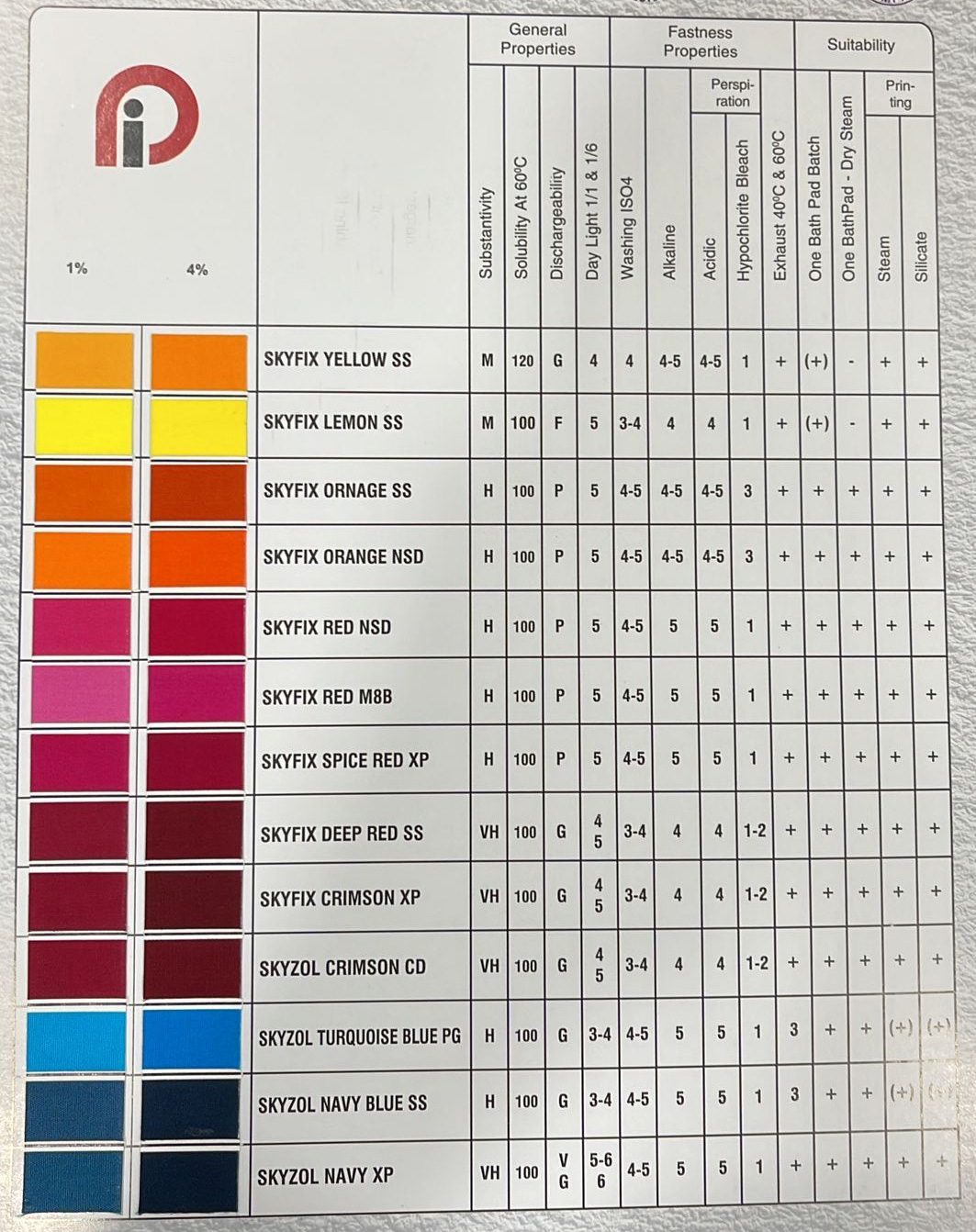
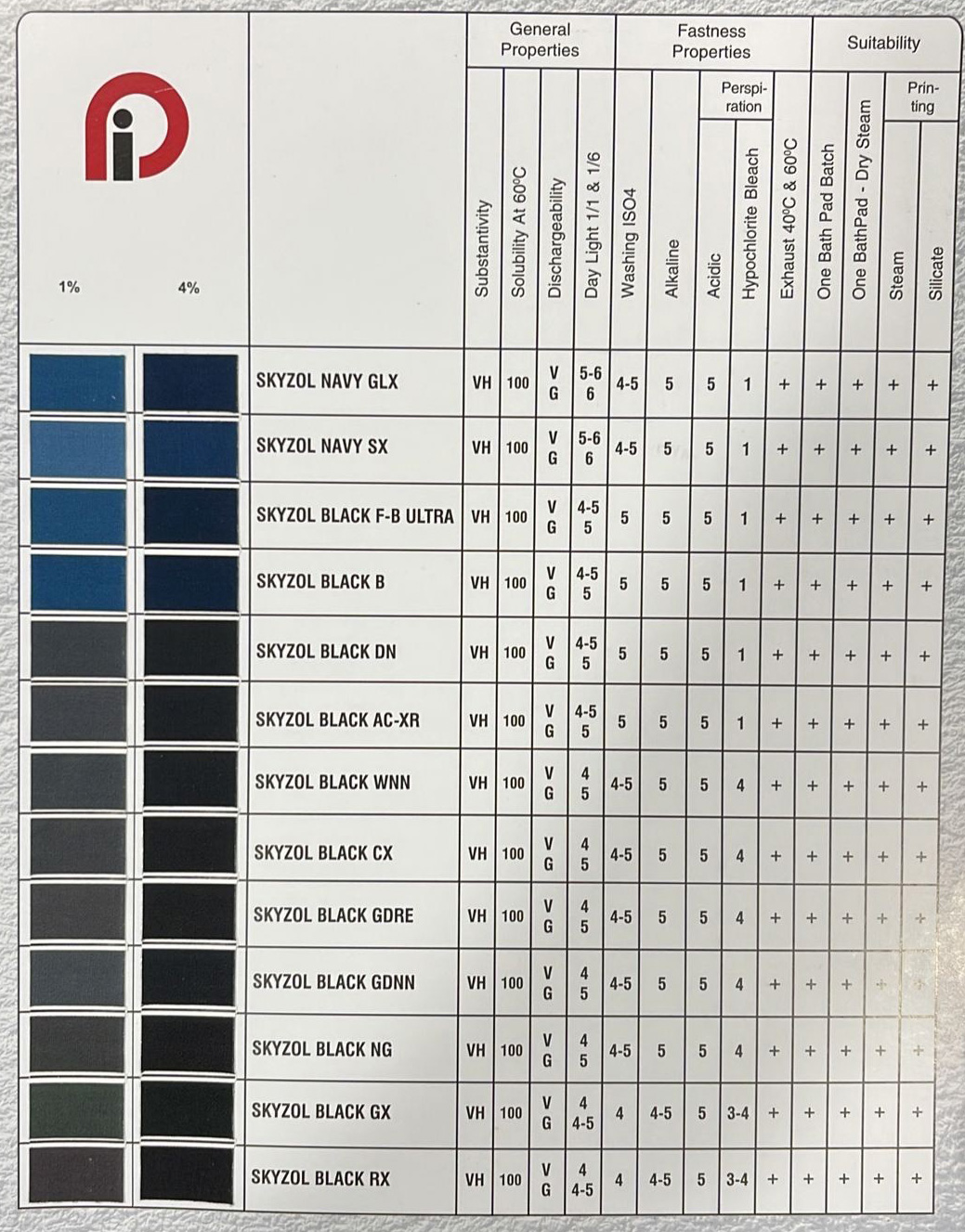
REACTIVE DYES MANUFACTURER IN INDIA
Pranav Industries Proudly 1994 in Manufacturer and Exporter of Reactive dyes and textiles Dyes Industries in Ahmedabad, Gujarat, India have a wide color range and are mostly used for printing cellulosic fibers such as cotton and linen. In reactive dye printing, dye molecules are diffused into the fibers and establish chemical bonds with them after fixation occurs. Although pigments are the most popular colorants in textile printing, reactive dyes are the most frequently used out of all other dyes, accounting for 30% of the total colorants used in the printing industry.
Unlike pigments, most dyes are substantive to fibers if the chemistry used in the coloration method is correct. Reactive dye printing chemistry requires an alkali, such as sodium bicarbonate, as the fixing agent to establish the molecular bonds between the dyes and the fibers. Printing with reactive dyes also requires a thickening agent. Sodium alginate thickener, a derivative of seaweed, is the most common. Other thickening agents, which are commonly used in other processes, are based on carbohydrates and would react with the dyes, creating poor printing results.
Fixation processes, which cure reactive dyes to the fabrics, generally include steaming the printed fabric with highly saturated steam followed by washing in hot water to remove the thickening agent and excess dye particles.
Reactive dyes manufacturer in ahmedabad, Gujarat, and India with Global Market have also become more widely used on polyamide materials as a means to produce dyeings and prints of excellent wash-fastness; additionally in the case of wool they exhibit a fibre protective effect which diminishes damage in dyeing and are also seen as alternatives to chrome dyes.
In addition to the detailed descriptions given in this chapter the reader is referred to very useful texts on reactive dyes and their application.
Reactive dyes manufacturers and exporter are a class of highly coloured organic substances, that attach themselves to their substrates by a chemical reaction that forms a covalent bond between the molecule of dye and that of the fibre. Reactive dyes are called so because this is the only type of dye that has a reactive group which reacts chemically with fibre part and form a covalent bond.